Server resources/resources
Hard disk
A hard disk is a place where persistent data is stored. These data is stored in files. Examples of such data might be world data (which is in the /world/ directory by default), player data, or plugin data.
Disk data manipulation
When editing or deleting files that are not configuration files (e.g. world files), it is important to do the editing always with the server turned off. Otherwise, changes may not be saved (in the case where data is later saved from RAM), or other problems may occur, such as corruption of the data being edited.
Disk types
A disk is essentially divided into two types - SSD and HDD. In simple terms, an SSD is suitable for a server and an HDD is suitable for backups.
HDD is better than SSD in terms of storage capacity and price, but it has a higher error rate and is slower compared to SSD. This difference is not negligible. The speed can have a significant negative impact on server performance and therefore SSD should be used as server storage.
On the other hand, HDD is ideal for storing backups.
Disk speed
Disk speed is an important feature up to a certain point. In particular, some standard VPS hosts tend to have very tight disk speeds. Therefore, even if the disk model is NVMe, it does not automatically mean that the disk is actually fast. Read more here.
Disk space usage
Unless the free disk space (not just the capacity available to you but whole disk) is critically low, disk space usage has no impact on server performance.
Normally, the world is the biggest consumer of disk space. For this reason, it’s a good idea to set a border (read more here). You can find out how much space a fully generated world with certains radius takes up by using this tool.
Then there are plugins that also take up a large amount of space. These include map webview plugins (Dynmap), or CoreProtect.
The size of the server data itself and the plugins is absolutely negligible compared to the data size of the world and plugins like Dynmap and CoreProtect. Therefore, the minimum disk space size should be based on the size of the world (and possibly plugins that take up a lot of space, if any is installed on the server), with some margin of course.
How to find out what takes up most space
If you have access to the server the Minecraft server is running on, there are many tools depending on the operating system you use to find out what is taking up the most disk space. For example, for Linux there is the ncdu tool (without GUI) or qdirstat (with GUI).
If you do not have access to the server, the admin (web)panels often provide a feature to view disk space usage/calculate folder sizes.
If you do not have access to the server and the admin panel does not allow provide feature to calculate folder sizes, the WinSCP FTP client (Windows only) allows you to calculate folder sizes.
Reduce disk space usage
Dynmap and similar plugins
Dynmap disk usage is affected by number of rendered worlds, its size, and map resolution. By deleting maps for unnecessary worlds and lowering the resolution, you can greatly reduce the disk usage of Dynmap.
The resolution can be set in the configuration
It is important to note that changing the resolution does not make the existing rendered data disappear, so changing the resolution itself does not free up space. Existing plugin data needs to be deleted. Only then will the disk space be freed.
CoreProtect
The size of the CoreProtect database depends mainly on the number of players and the configuration of what all CoreProtect logs.
The purge command allows you to delete old data, which frees up the disk space. For example, the co purge t:30d command will delete all data older than one month, see https://docs.coreprotect.net/commands/#co-purge.
Deleting inactive chunks
In particular, if you don’t have a world border set (and thus the world size is unlimited), the MCASelector utility can be useful to delete “inactive” chunks, meaning chunks that are generated (i.e. taking up disk space), but the player has only been in them for very small amount of time (e.g. flew through them with elytra). This can free up quite a lot of space, especially on servers that have been around for a long time. This tool is written in Java and has a CLI version, so if you have the ability to edit the startup command, the tool can be used directly on the server where the world is located. If you don’t have that option (to change startup command), you can try asking support if they couldn’t run it. When the answer is no, you need to download the world, install the tool, use it, delete original world, and upload the modified world back to the server.
Standalone database
In the case where you have a standalone database, and a plugin that takes up too much disk space has that option, you can use a database as a storage, which frees up disk space (after deleting the data on the disk). This is of course not the case if the disk space used by the server also belongs to the database itself, e.g. if you have a VPS server where you host both the server and the database.
If the database is provided as an additional service, the database often has a smaller maximum size per database (typically 1 GB). In this case, the database is not suitable for plugins that use a lot of space, as such plugins takes up a lot more space. Connecting plugins like LuckPerms to standalone database is useless in terms of saving disk space, as such plugins take up almost no space.
Disk space is full
When SSD space fills up very quickly for no apparent reason, the cause is most often a spammed log. Therefore, in this case you should first look in the /logs/ folder for the size of the log files. If their size is in the hundreds of megabytes, or even gigabytes, this is a problem that needs to be resolved. Logs should be in units of MB, at most a dozen (but even that is a lot, and the log is spammed with errors you should fix).
The most common cause of an extremely spammed log is using a new version of Java for old Minecraft versions, but the cause of a spammed log can be a plugin or a mod too.
Memory (RAM)
RAM is the memory that temporarily stores the data the server works with. Persistent data is later saved to disk. The moment the server needs to work with the data, they are loaded into memory.
RAM usage/keeping RAM (GC)
The pattern of heap memory usage behavior is that it fills up, and after some time it frees up (see the figure below). The fact that memory is filling up and freeing up does not indicate anything wrong. This is standard behavior in garbage collected languages.
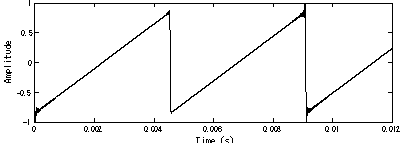
Also, the fact that most of memory is used doesn’t mean anything bad either. In short - Java will use what it can. This is even more noticeable when using (optimized) Aikar flags. Because up to a certain point, unused memory is “wasted” memory, and perhaps you want to use what you pay for.
See this section for how to tell if you have enough memory.
What is heap memory
Heap memory is the memory where all Java objects that are used by the Minecraft server itself are stored. This can be loaded chunks, player information etc. The size of heap memory that can be used by the server is determined by Java flag Xmx.
Memory needed
-
heap memory is the memory that can be used by the Minecraft server itself. How much of this memory the server can use is determined by startup flag Xmx
-
Java memory
For Java applications to work, it is not enough to have only heap memory available, but also some extra memory for Java itself.
- Memory for the operating system - If you are managing the server running Minecraft yourself, you need to make sure you leave enough memory for the operating system itself and the other processes running on it.
In the case where the server is running in a container (Docker), you don’t need to consider spare space for each container, as a container is just an isolated environment and not a virtual machine where a separate operating system runs for each instance.
The PaperMC documentation says (edited):
“Do not allocate all of your available memory on a shared host!
When setting the Xms and Xmx values, if your host says you have 8GB of memory, do not use 8GB!
Minecraft (and Java) needs additional memory on top of that Xmx parameter. It is recommended to reduce your Xmx and Xms by about 1000-1500MB to avoid running out of memory or OOMKiller killing your server. This also leaves room for the operating system to use memory too.
Do you have 8GB of memory? Use 6500MB for safety. But you may also ask your host if they will cover this overhead for you and give you 9500M instead. Some hosts will! Just ask.“
Memory indicators (memory vs memory)
When talking about memory (RAM), it can be very important what kind of memory is being talked about. You may encounter the following:
- heap memory used
this value is shown by the Spark profiler and is a value indicating the current heap memory usage. This is almost always the only value you are interested in and is useful. When we talk about used memory, we usually mean this value.
- heap memory size
in this case two values can be meant - the current size of (allocated) heap memory, or the maximum heap memory size. What is the difference between these values can be found here. Usually we mean the maximum heap size (Xmx flag, i.e. how much heap memory can the Minecraft server use)
- system indicator
if you are looking at the memory usage values via the admin (web)panel (Pterodactyl) or a system command (top, htop, ps)/Task Manager, this value is almost always irrelevant.
However, on some hosts you may have a plugin/mod installed that communicates with the panel, so you will see the same value in the admin panel as Spark would show (heap memory used).
Amount of memory
important
All values given in this section denote the heap memory, which max size is determined by Xmx flag, i.e. memory for Java and the operating system is not included. Read more about the differences between these values here.
The values shown are intented for 1.21. Older versions (=< 1.12) can easily get with less RAM and the requirements will increase over time.
Impact of memory on performance and lack of memory
If you have at least 6 GB (actually even less memory like 4 GB should be fine) of heap memory allocated on a small to medium sized Paper server and you have a noticeable server performance problem, the problem is probably not lack of memory. Although providing more RAM would improve performance in the case of 6 GB, there is almost certainly not so little memory to cause a significant negative impact on the server performance. From 10 onwards, you can be almost always sure of this (except for extremely memory heavy servers). You can read more about server performance here.
So as far as Paper is used, allocating more than 10 GB of heap memory is (except for really large and heavy servers) almost always unnecessary, regardless of the number of players and plugins. For modded servers, this limit is pushed a bit higher, but still, from a certain point on, increasing RAM doesn’t help with performance.
You can find out how to determine if you need more memory in this article: https://docs.pufferfish.host/general/why-is-my-ram-all-used/#how-do-i-know-if-i-need-more-ram
However, insufficient memory can have a significant impact on server performance.
If you feel that giving server more memory has solved performance issues on shared host, keep in mind that even if the CPU performance is not specified, plans can vary not only in terms of memory, but also in terms of CPU performance. Thus, the problem may not have been solved by increasing RAM, but by better processor performance. This may be more noticeable on Vanilla and especially modded servers.
Lack of RAM absolutely does not affect the functionality of various aspects of the game, such as plugins.
Too much memory
If you want to increase the memory because of the (almost) 100% memory usage shown by the admin (web)panel (Pterodactyl) or the system indicator (htop/Task Manager), it doesn’t mean there is not enough memory. Read more here.
As noted in the PaperMC documentation, more memory from a certain point does not mean better performance. Unfortunately, this is an ongoing myth stemming from a misunderstanding of how Minecraft server (Java application) memory works and hosting companies’ desire to maximize profits.
Buying server with 32GB of RAM will not help you in terms of performance and is just a waste of money. The server has no way to use that much memory. Conversely, from a certain point where there is too much RAM, performance declines.
That means that, for example, the following comment is completely false: “Hi, 8 GB of RAM for server is very little. I have a dedicated server with 64 GB of RAM and believe me, even 64 GB is not enough. For example, my server can hold about 30 to 45 players with 64 GB of RAM. Considering you have 8 GB, even 5 players is too much.”
Until RAM is severely lacking, the the bottleneck is usually the CPU.
Minimum recommended memory
important
This is only my personal recommendation based on experience. Some might disagree. This section might and probably be edited or even deleted.
Please note that the stated values are for reference only. It is not possible to say in general how much RAM is needed as a minimum, as it depends on many factors such as platform number of players, optimization, server type (e.g. Survival will need more RAM than BedWars server), plugins or mods used, etc.
Paper and its forks
The PaperMC article says: “We recommend using at least 6-10 GB, regardless of the number of players! If you can’t afford 10 GB of memory, give as much as you can, but make sure to leave some memory for the operating system as well.”
So if you have that option, give the server at least 6GB of memory if you can. If you can’t afford that much memory and it’s not a performance heavy server, especially in terms of player count, you can run the server on 5, 4, or even 3 GB of RAM, but the more memory the better.
Technically speaking, you are able to run a server for a few friends on 1.21 even on 2 GB RAM (still talking about heap memory only!), however, you may need to optimize the server and perform regular restarts. However, this is definitely not ideal and I would take at least 3 GB of RAM as a recommended minimum, 4 if you can.
However, as Paper states, at least 6 GB of RAM is recommended.
Vanilla
Vanilla is generally less capable of running with less memory than Paper, so the minimum limit is pushed a bit higher.
Modded server
A modded server is the kind of server that generally requires the most RAM. This amount can vary significantly depending the mods. Thus, the minimum memory required varies depending on the modpack, and can be up to several GB more than Paper for heavy modpacks.
Proxy
Proxy servers does not require much memory, so the vast majority of proxies can get by with 1 GB of RAM. For example, the Velocity documentation states that 2 GB of memory should be allocated for 1,000 players.
Memory usage
It may not be easy to create a realistic mental model of how much memory different parts of the server use, especially if you have no idea how the server technically works “under the hood”. Therefore, below is some basic information about how different aspects of the server impact memory usage.
Worlds
Each player has an area (circle) around them. One area determines how far the player can see. This affects the view-distance setting in server.properties.
Then the area whose size is determined by the simulation-distance value in server.properties.
The size of these regions has a major impact on memory usage, as they determine the size of the area around each player for which the chunks themselves will be loaded and updated (ticked). That means updating all entities, plants, blocks and so on.
It is the number of chunks loaded and all the actions performed in them that has a significant impact on memory usage.
This is why, for example, a BoxFight or BedWars server will use noticeably less memory than Survival server.
Thus, if a server had 70 players in one place, it would use significantey less memory than a server with 70 players spread all over the world. At the same time, on a server with 70 players, adjusting the simulation distance would also have a noticeable impact on memory usage, as the number of chunks updated would increase noticeably.
As explained, the number of chunks loaded is crucial. The number of worlds doesn’t play that much of a role. While each world has spawn chunks that are automatically loaded even when no one is in the world, the number of these chunks is not very insignificant (also it’s possible to disable the loading spawn chunks in Paper config).
Plugins
The amount of memory required to load a plugin is insignificant, so the number of plugins does not play a major role in memory usage. Much more crucial is how much memory a particular plugin needs and what it does. A single plugin can use much more memory than dozens of other plugins combined. Examples of such plugins include Dynmap, or Chunky when generating chunks. However, if Chunky does not generate any chunks, it uses almost no memory (the generation task is what use the memory). So it depends on what a particular plugin does.
Xmx and Xms flags
The Xmx flag specifies the maximum available heap memory size. The Xms flag specifies the size of the heap memory the process starts with, so the heap memory size cannot go below this value.
Current and maximum heap memory size
The Spark profiler shows the current usage (shown on the left) and size (shown on the right) of the heap memory.
This means that if Xmx is set to 8 GB and Xms is set to the same, Spark will always show a heap size of 8 GB, since that is the size of memory allocated (since the process starts with that value, which as mentioned, is determined by the Xms flag, and the heap size cannot go below that value).
In the case that the Xms value is lower than the Xmx value, this does not apply. Let’s say the maximum memory size is still 8 GB and Xms is reduced to 1 GB.
This means that Java allocates 1 GB of heap memory at the beginning, and when it needs it, it allocates more (maximum of Xmx, which is 8 GB in this case), thus the heap memory size increase. Thus, the heap memory size can range from 1 to 8 GB.
Should Xms be equal to Xmx?
It used to be very strongly recommended that Xms should equal Xmx. Hosting providers lower the Xms value to make fit more servers per node.
Nowadays, Java behaves differently, so a lower Xms value is not a big deal. Even so, the same Xms value as Xmx can still help in terms of performance. However, if you don’t have that option, it’s not as crucial as it used to be, so you probably don’t need to worry about it.
Memory leak
As written on Wikipedia - In computer science, a memory leak is a type of resource leak that occurs when a computer program incorrectly manages memory allocations in a way that memory which is no longer needed is not released.
If you suspect a memory leak because a panel/system indicator (e.g. htop/Task Manager) shows (almost) 100% memory usage when there should be enough memory, it is not a memory leak. See here for more information.
However, if you have 6 to 10 GB of heap memory allocated on the Paper server, enough memory for Java and the operating system itself, and the server crashes after some time due to lack of memory (OutOfMemory error), the chances that there is memory usage without freeing memory is quite high, since with a small number of players, this amount of memory should be quite sufficient.
How to recognize and solve a memory leak can be found at the following link: https://docs.pufferfish.host/general/why-is-my-ram-all-used#what-is-a-memory-leak
The command spark heapsummary can be useful too.
CPU/Processor
The CPU is the “brain of the computer” that processes and executes all tasks.
CPU model
For the CPU of a Minecraft server, the most important CPU parameter is the single thread performance. A Minecraft server cannot use multiple threads efficiently, as the main game loop runs on one thread only (this does not mean that it does not use more than one thread - the minimum recommended number of threads is four, see below for more information). This is why traditional VPS hosts are not suitable for hosting Minecraft servers - there are many threads available, but these threads are has low performance per core. (see here).
As stated in https://paper-chan.moe/paper-optimization/, when selecting a processor, do not use clock speed to compare two processors (unless they are the same model and manufacture): “When selecting CPUs for your Minecraft server, do not use the clock speed rating to compare two CPUs unless they are of same model and manufacture. Please refer to Gigahertz Myth for more info. In short, select the latest CPU architecture and the highest single core thread rating model available.”
Thread count
Although single-thread performance is essential, as stated in https://paper-chan.moe/paper-optimization/, the minimum recommended thread count is 4: “The minimum recommended thread/core count for a Minecraft server is FOUR. While it is true that the main game loop is done entirely on a single thread, there are many tasks that can benefit from multiple threads. For example, Netty, plugins, SQL databases, etc.” (edited)
However, from a certain point, assigning more threads will not bring any benefit. It is still the performance of a single thread that matters the most. Assigning 32 cores to a server will not help performance (does not apply to Folia platform).
Too high CPU usage (up to 100%)
In the case where you have enough CPU resources available, but the performance is not sufficient, make sure you have the appropriate CPU model for the Minecraft server.
If you’re using a traditional VPS hosting service, the CPU is probably not suitable for a Minecraft server. Read more here.
High CPU usage can also be caused by plugins. This happens often for example with Dynmap, which can use up to 100% of the CPU (in the sense of all available CPU power, not a single thread) during (automatic) rendering. You can read how to solve this here.
Connectivity
Connectivity refers to the interconnection of devices (computers).
The most important factor of connectivity is usually its stability and speed that is usually stated in Mbps (megabits per second), but you may also see MB/s (megabytes per second; or MBps, which is the same as MB/s).
Mb (megabit) and MB (megabyte) are different units. A megabit is one-eighth of a megabyte. This means that 8 Mbps is equal to 1 MB/s.
Fortunately, you will only be concerned about connectivity if you are hosting the server yourself at home, as internet speeds may not be sufficient if your internet is slow. The connectivity provided by hosting services is almost always absolutely sufficient for a Minecraft server, and so it is usually not even listed.