How to deal with issues
To learn how to troubleshoot basic server issues, see the following link: https://docs.papermc.io/paper/basic-troubleshooting and below.
If you are experiencing a problem with a server, plugin (or mod), the cause of the problem can almost always be read from the server log. If you are not able to understand the contents of the log even after sufficient (or at least minimal/basic) effort, just ask for help.
If you can’t tell the cause from the log, disable all plugins to find out if the problem is caused by the plugin or by the platform itself (if the problem disappears after disabling all plugins, it is logically caused by the plugin).
If the problem is caused by a plugin, use binary search to find out which one (and update/report the plugin if necessary).
If the error is caused by the server platform itself, update it as well and report the error if applicable.
If it’s not a problem (bug) but you don’t know how to handle a certain behavior/setting of the plugin, you can almost always find everything you need in the platform/plugin documentation, or you can find it in the configuration, eventually you can contact the plugin author/support. If you want to allow certain actions for specific/all players, learn how to work with permissions.
Binary search
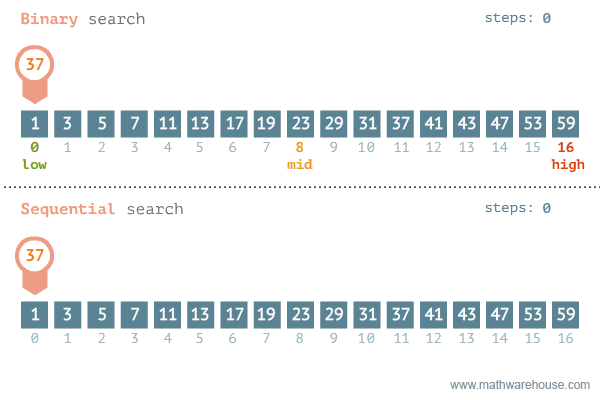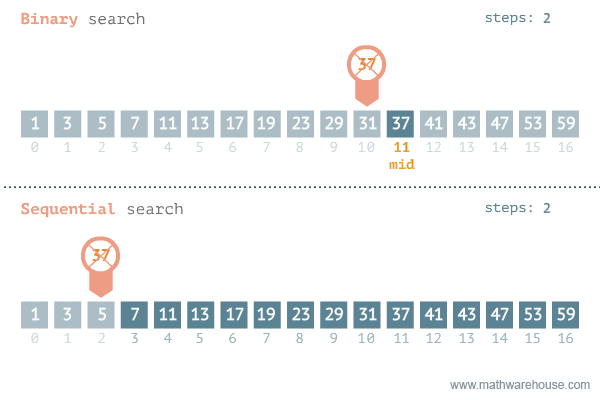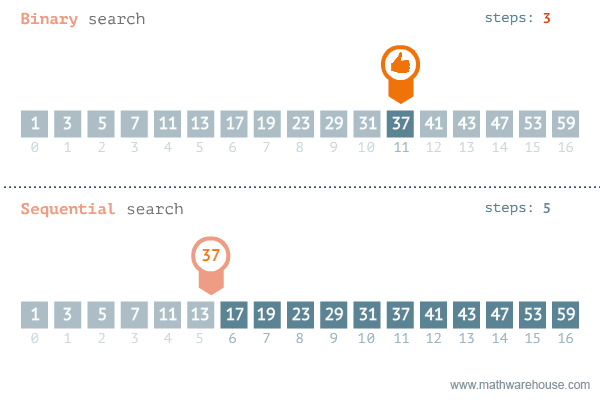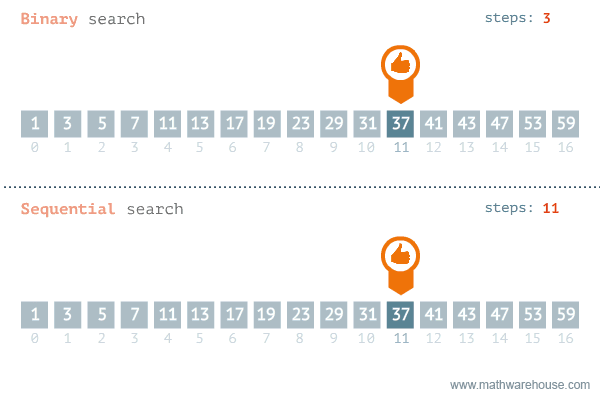
In the case where you don’t know what plugin (or mod) is causing the problem, but you know that a plugin is causing it, the most efficient method to find the plugin is by using the binary search method. How this method works and how to perform it can be found at the following link: https://docs.papermc.io/paper/basic-troubleshooting#binary-search
For modded servers, the binary search can be more tedious, as the server is likely to crash (shut down) if a dependency is missing. In this case, you have to find the missing dependency in the log and move it back to active modes (and not remove it until the mod that requires it is in active mods). At the same time, the server mod list and client most list may need to be synchronized, so the mods will need to be removed not only from the server but also from the client.
The binary search method is much faster for searching through larger lists than going through plugins one by one. For example, if there were 100 plugins on the server, you would need 73 attempts if you were disabling plugins one by one, if the faulty plugin was 73rd. However, if you use the binary search method, you need a maximum of 8 attempts (100 -> 50 -> 25 -> 12 -> 6 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1).
How to do XY / What is the permission for XY / What is the placeholder for XY / What is the command for XY
As described in this section, the various functions, perms, placeholders and commands are always plugin specific. Although plugins share many common principles, these things should always be looked up in the documentation of the plugin or platform.
Action and reaction principle
When you add a plugin, execute a command, and the server starts to, crash, something stops working, etc., the logical first thing to do is to check if the action isn’t the cause of the problem.
So, if a problem occurs after an certain action has been performed, you should suspect that the action is the cause first.
Advanced
Searching in source code
If you understand programming, it may be useful to read the source code in certain cases.
If the project is open-sourced on GitHub, you can rewrite ’github“ to ’github1s“ in the project URL and pressing Enter will open the project in a web editor. You can do the same by rewriting github.com to github.dev, or by pressing the . (dot) character in the GitHub repository, which will redirect you to the repository in the github.dev editor. Both github1s.com and github.dev have identical functionality, github.dev is the official GitHub platform (I personally prefer github1s as I find it more nimble).
In this text editor, you can easily search across all the files in the project (top left 3 vertical lines under the GitHub logo -> Edit -> Find in Files).
In the case where the plugin is not open-source, you can decompile the plugin using a Java decompiler like JD-GUI, but this may violate the TOS (terms of use) of some plugins (especially paid ones).
Finding configuration files in source code
Configuration files can be found in the source code in /src/main/resources/, so for example for EssentialsX they can be found here.
If a plugin supports multiple platforms, these files are usually in a shared folder that all these versions of the plugin use, as in the case of the plugin TAB (by NEZNAMY), where these files are located in the shared folder (but it’s often called something else, such as common) see https://github.com/NEZNAMY/TAB/tree/master/shared/src/main/resources/config
However, sometimes the plugin does not contain such files, or not all files do. For example, for this plugin the basic configuration is hardcoded in code instead of bein in separate file.
Changelog
The changelog describes a list of changes, i.e. new features, bug fixes, vulnerabilities and other changes. For this reason, it is a good idea to check the changelog when updating the plugin so that you don’t miss important updates. However, the changelog can also be useful when troubleshooting various issues. There are many cases where the changelog comes in handy. One such specific example is with the Citizens plugin, which only supports the latest subversion (i.e. when support for 1.20.2 is released, 1.20.1 is no longer supported). So if you would like to use a version that supports 1.20.1, you need to find the build in the changelog when the version supporting 1.20.2 was released, and thus download the last build released before that version (supporting 1.20.2).
You will find the changelog different on each platform where the plugin is released, but you will almost always find it somewhere, for example:
- Spigot - Updates tab (example)
- Modrinth - Changelog tab (example)
- Jenkins - Changes tab (example)
- GitHub - Releases tab (example)
If the server platform changes are not on the platform page, such as for Paper, you should at least find the changes in GitHub Releases (e.g. here), or Git commits on the platform where it is developed (this is for Paper GitHub, for Spigot Jira, for some it may be GitLab).
If the software is open-source, in the commits on the platform where the project is developed (GitHub, GitLab, Jira, Gitea, …) you will find all the changes, regardless of whether it is a platform, plugin, or mod (since that is how software is generally developed).
Search
Whether you’re looking for how to do certain a thing, for a plugin, mod, cause of a specific bug or source (config/part in documentation/…), etc., usually the ideal way to find what you need is by using Google.
Discord searches can also help. There are plenty of messages on active Discord servers, so the chance someone has asked the same question is high. Therefore, before you ask a question in a Discord channel, it is a good idea to check if you can already find a message with a similar question/problem.
Below are some general beginner tips that may help you.
Google search (tips)
When searching for a particular bug, copy only the relevant part, i.e. the text that is the same for all, i.e. for a bug only the error message itself without the time, log level etc., in short only the relevant part to the bug.
If you’re looking for a specific thing like a plugin, its particular settings or config, simply search using keywords like “<plugin name> config.yml”, “minecraft ban plugin”, etc. (see plugin search)
Strict search / Exact search
If you only want Google to return results with exact match, simply enclose the search text in normal quotes ("strict search").
Discord Search (tips)
When searching for text on Discord, search by keywords that may have been used in the question/issue description. Of course, words can be used in different forms, which is good to keep in mind and try multiple variants if you can’t find what you are looking for on the first search.
It’s good to keep in mind that when using keywords in a search, the words don’t have to be next to each other, but their order matters.
In Discord searches, the diacritics matter.
Of course, the more relevant to the problem (i.e. if you have a problem with a plugin and the plugin in question has a Discord server, it’s ideal to start your search there) the Discord server in question is, and the more messages it contains, the better.
Translator
If the text is in a foreign language you don’t understand, use a translator like DeepL, or the classic Google Translate.
When you enter a URL (link) into Google Translate, you can then click on the URL and the whole page will be translated (there are also browser extensions that will translate the page). Eventually, your browser may have this feature built in.
Text search
Whether it is a text editor or a browser, you can almost always search text in a program using the Ctrl + F shortcut (do not use the F3 key).
In the case where you are looking for a particular thing but don’t know exactly what it is called, try searching using keywords.
In the configuration files, watch out for colors and variables when searching in the text.
When copying some text from the internet you want to search for, be careful not to copy a space at the end or beginning of the text, which sometimes happens when you double-click to select the text. In case that would happen, make sure to remove the space(s) from the text, otherwise you may not find anything in the text, even if the text you are looking for is in the text but without the space(s).
Reading stacktrace
You can read what a stacktrace is here. When reading stacktrace, it is useful to have basic knowledge of Java. All the terms used in this section can be found in the Java basics chapter.
Below are specific examples of stacktraces and what the thought process might look like when reading it. The ability to solve a problem using stacktrace depends on your experience and knowledge, and you will probably get better at it over time.
Examples
Example 1
[16:55:29] [Server thread/ERROR]: Encountered an unexpected exception
org.spongepowered.configurate.serialize.SerializationException: [entities, spawning, monster-spawn-max-light-level] of type java.lang.Integer: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "default"
at org.spongepowered.configurate.serialize.NumericSerializers.parseNumber(NumericSerializers.java:346) ~[configurate-core-4.1.2.jar:?]
at org.spongepowered.configurate.serialize.NumericSerializers.lambda$static$9(NumericSerializers.java:254) ~[configurate-core-4.1.2.jar:?]
at org.spongepowered.configurate.serialize.FunctionScalarSerializer.deserialize(FunctionScalarSerializer.java:40) ~[configurate-core-4.1.2.jar:?]
at org.spongepowered.configurate.serialize.ScalarSerializer.deserialize(ScalarSerializer.java:115) ~[configurate-core-4.1.2.jar:?]
at org.spongepowered.configurate.objectmapping.ObjectMapperImpl.load0(ObjectMapperImpl.java:64) ~[configurate-core-4.1.2.jar:?]
....
at io.papermc.paper.configuration.Configurations.initializeWorldDefaultsConfiguration(Configurations.java:154) ~[paper-1.20.1.jar:git-Paper-196]
at net.minecraft.server.dedicated.DedicatedServer.initServer(DedicatedServer.java:210) ~[paper-1.20.1.jar:git-Paper-196]
at net.minecraft.server.MinecraftServer.runServer(MinecraftServer.java:1100) ~[paper-1.20.1.jar:git-Paper-196]
at net.minecraft.server.MinecraftServer.lambda$spin$0(MinecraftServer.java:317) ~[paper-1.20.1.jar:git-Paper-196]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:833) ~[?:?]
This stacktrace starts with exception, which throws Configurate. What even is this Configurate? You can easily find out by googling the software/library name and the project/author name (both of which you can read from package, in this case org.spongepowered.configurate). So in this case, just use Google to search for “spongepowered configurate “. You will find out that “Configurate is a simple configuration library”. So it is a library for working with configuration files.
So the name of the exception SerializationException indicates that there was an error when serializing the configuration, or in simple terms, loading it. Specifically, an error occurred while serializing the value entities.spawning.monster-spawn-max-light-level (written using dot notation).
This error occurred because a NumberFormatException occurred, as Integer (number) was expected, but the value of the field was “default” (which is String instead of Integer).
So now you know that the value of some field is default, even though a number was expected.
But now how to find out which configuration file it is? In this case, there are two easy ways to find out:
- from stacktrace
at io.papermc.paper.configuration.Configurations.initializeWorldDefaultsConfiguration(Configurations.java:154)...
- using Google
When you search for “monster-spawn-max-light-level” (with quotes for strict search, without it you would probably come across a lot of irrelevant results), the following page will pop up: https://docs.papermc.io/paper/reference/world-configuration
Both of these tell us that the entities.spawning.monster-spawn-max-light-level field with the value default is in the Paper world config, whose location is /config/paper-world-defaults.yml.
Okay, now you know that the value of the entities.spawning.monster-spawn-max-light-level field is default, even though a number is expected. But why did this happen? Practically, this could mean two things:
- Someone manually set the value of this field to
default- that probably didn’t happen. - The value of the
defaultfields was set automatically, no one set it manually
Basically always option 2 was the cause of this error. This happened when downgrading a server, where the Paper config was generated on a newer version that supported the default value, but the user was using an older version that didn’t, so the only valid value was a number.
(Eventually Paper could contain a bug, but that is very unlikely)
Great, now you even know why the problem occurred, but how to solve it? Logically, there are two solutions to this situation:
a) Manually set the value of entities.spawning.monster-spawn-max-light-level (and all other fields with the value default) from default to a number (you would find the default field values in the PaperMC documentation).
b) Delete the config and let server automatically generate new (default) one.
So the solution is to reset the Paper config or set the fields with the value “default” to valid (numeric) values.
2nd example
.....
[12:32:13] [Server thread/INFO]: [HeadDatabase] Loading HeadDatabase v1.2.0
.....
[12:32:21] [Server thread/ERROR]: [DeluxeHub] Plugin DeluxeHub v3.5.5 has failed to register events for class fun.lewisdev.deluxehub.hook.hooks.head.DatabaseHead because me/arcaniax/hdb/api/DatabaseLoadEvent does not exist.
[12:32:21] [Server thread/ERROR]: Error occurred while enabling DeluxeHub v3.5.5 (Is it up to date?)
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: me/arcaniax/hdb/api/HeadDatabaseAPI
at fun.lewisdev.deluxehub.hook.hooks.head.DatabaseHead.onEnable(DatabaseHead.java:20) ~[DeluxeHub-3.5.5.jar:?]
at fun.lewisdev.deluxehub.hook.HooksManager.lambda$new$0(HooksManager.java:35) ~[DeluxeHub-3.5.5.jar:?]
at java.util.stream.ForEachOps$ForEachOp$OfRef.accept(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
at java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$2$1.accept(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
..........
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source) ~[[?:?]
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: me.arcaniax.hdb.api.HeadDatabaseAPI
at org.bukkit.plugin.java.PluginClassLoader.loadClass0(PluginClassLoader.java:153) ~[server.jar:git-Purpur-1428]
at org.bukkit.plugin.java.PluginClassLoader.loadClass(PluginClassLoader.java:105) ~[server.jar:git-Purpur-1428]
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
... 23 more
[12:32:21] [Server thread/INFO]: [DeluxeHub] Disabling DeluxeHub v3.5.5
In this log you will encounter a stacktrace with the error NoClassDefFound. The DeluxeHub plugin is trying to work with the HeadDatabase plugin, specifically its class me/arcaniax/hdb/api/HeadDatabaseAPI. The log also says that the HeadDatabase plugin is installed and enabled on the server, so the problem cannot be the missing plugin.
So DeluxeHub tries to work with the class plugin, which is on the server, but does not have a specific class. This can mean the following:
- DeluxeHub is working with a different version of the plugin
This is usually the most common cause for plugins, but this is the case here This is not the case here.
- HeadDatabase plugin installed on the server is not HeadDatabase plugin DeluxeHub expects
Typically, dependencies and links to them should be listed on the plugin page. This is not the case with DeluxeHub, but you can easily tell which plugin DeluxeHub is trying to work with from the stacktrace. You can find the specific plugin by Googling the plugin name and the name package.
This allows you to find out that it is this particular plugin: https://www.spigotmc.org/resources/head-database.14280/, but there is a completely different plugin on the server called HeadDatabase installed, specifically this one https://www.spigotmc.org/resources/headdatabase.95118/, which you can find out by searching “HeadDatabase 1.2.0” in Google.
What is the solution in this case? First, I would look into the plugin configuration to see if the HeadDatabase hook can be disabled (to prevent DH from trying to work with HeadDatabase). DeluxeHub doesn’t have that option, so the only thing to do is to report this to the DeluxeHub developer and hope that they fix this issue, or remove the plugin (which in this particular case would be the most sensible option, since it is an outdated, unmaintained plugin that you probably don’t even want to use and have it on your server “by mistake”) (or, since HeadDatabase is an open-source plugin, you could possibly change the name of the plugin if you are able to. This would resolve the DeluxeHub error, since DeluxeHub would not try to work with the “HeadDatabase” plugin, since a plugin with that name would not be on the server).
3rd example
[19:37:03] [Server thread/ERROR]: Could not load 'plugins/UltraStaffChat-5.2.2.jar' in folder 'plugins'
org.bukkit.plugin.InvalidDescriptionException: Invalid plugin.yml
at org.bukkit.plugin.java.JavaPluginLoader.getPluginDescription(JavaPluginLoader.java:178) ~[paper-api-1.18.2-R0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar:?]
at org.bukkit.plugin.SimplePluginManager.loadPlugins(SimplePluginManager.java:159) ~[paper-api-1.18.2-R0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar:?]
at org.bukkit.craftbukkit.v1_18_R2.CraftServer.loadPlugins(CraftServer.java:418) ~[paper-1.18.2.jar:git-Paper-388]
at net.minecraft.server.dedicated.DedicatedServer.initServer(DedicatedServer.java:288) ~[paper-1.18.2.jar:git-Paper-388]
at net.minecraft.server.MinecraftServer.runServer(MinecraftServer.java:1164) ~[paper-1.18.2.jar:git-Paper-388]
at net.minecraft.server.MinecraftServer.lambda$spin$0(MinecraftServer.java:316) ~[paper-1.18.2.jar:git-Paper-388]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException: jar does not contain plugin.yml
... 7 more
In this stacktrace you will encounter the error “Invalid plugin.yml”. The cause of the error is directly stated as “Jar does not contain plugin.yml”. You can read why this error occurs here (or just type the error into Google and you will find many posts on this topic).
In this example, it is a BungeeCord plugin.